Site Semantic Core (SSC) is a set of phrases that describe the website, its theme, and direction. For very large websites, the semantic core can contain several thousand keywords. Regardless of the promotion method you choose—SEO or contextual advertising—you must start with collecting queries.
ORDER contextual advertising setup
Why?
Because compiling a list of queries and distributing them across the pages of your site is the first and main task without which you cannot start further website promotion. If you have chosen SEO promotion, skillful work on the semantic core will allow you to successfully raise your site to the top of search results. If you have chosen contextual advertising, on one hand, you will already have a list of queries to use in your campaign; on the other hand, landing pages that the ads lead to will be optimized for these queries, reducing cost per click and thus saving your money. Therefore, creating a semantic core is simply essential.
Compiling the Semantic Core
You can compile a proper semantic core in several steps:
- First, you need to identify queries that describe your site and its content. You can use services like Google AdWords. There are also programs for automating such query collection, for example, KeyCollector.
- After the initial basic stage, filter out irrelevant queries that do not fit your advertising campaign or SEO promotion. These are queries that do not correspond to your site’s content.
- Remove queries with low base frequency, as they will not have much effect in both advertising campaigns and SEO promotion.
Types of Queries:
High-Frequency (HF) — general queries that do not reveal user needs (“phone”). Typically, such phrases are searched for 10,000 times per month or more (of course, this depends on the display region).
Medium-Frequency (MF) — refined HF queries (“buy phone”). Within a few thousand, sometimes 500-900 people per month. There is no definitive opinion, so you can decide for yourself and your niche what frequency is average.
Low-Frequency (LF) — highly specific queries (“buy green BMW car”). Such queries are entered into the search engine by approximately 100-200 people per month, but they provide the highest conversion because users are highly interested in the search subject.
Queries can also be categorized as high-competition, medium-competition, and low-competition. The level of competition should be determined individually in each niche. The more sites in the search results for your query, the higher the competition. The same situation applies to contextual advertising— the more sites advertising for the chosen query, the higher the cost per click.
When creating a semantic core, consider the following:
Your list of key queries should include both general and specific terms. If you focus only on LF queries, the traffic will be more targeted but minimal. Conversely, if you emphasize HF queries, traffic relevance cannot be guaranteed, and there are many sites in the search results for such queries, making it difficult to reach the top of search results. Therefore, creating a semantic core requires a balanced approach.
Use associative queries and synonyms that users might enter. This way, you can attract targeted traffic to your site by carefully working on the semantic core. If your competitors haven’t done this, it will be easier to reach the top, and in the case of contextual advertising, you can reduce the cost per click.
Creating the Semantic Core
Now, let’s move on to practical steps—forming the semantic core. Various services can help you create the semantic core of your site. Google Keyword Planner is one such service, and Google’s Keyword Planner is another, along with many other services. Today, we’ll look at the basic one you need to master—Google Keyword Planner.
This service will help you obtain statistics on all queries that users enter into the search engine. Moreover, Keyword Planner displays associative queries separately, which is its advantage.
Let’s illustrate the algorithm of actions. If your site sells smartphones, you need to start selecting keywords on this topic. Open a notepad and write down queries that can represent your niche. For example: buy smartphone, buy Samsung Galaxy smartphone, Samsung Galaxy S5 smartphone, Samsung Galaxy S5 smartphone price.
After that, sequentially insert all phrases from your list into Keyword Planner. The system will automatically generate all possible variations based on the query you entered. Initially, you should select the display region for which you will gather statistics.
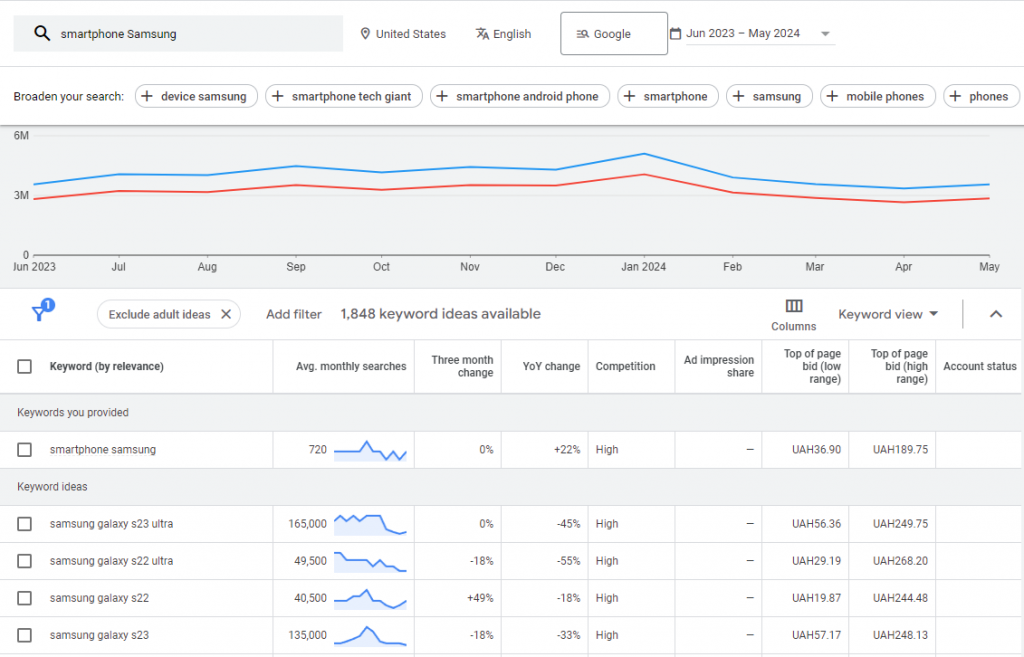
That is, you need to enter general queries based on “brainstorming,” and Keyword Planner will gather possible keyword variations that users have entered over the past month based on your query.
Here’s another thing to understand – types of matchings. For example, when you simply enter a query, the system collects all variations based on your query, including adding other words, word forms, and changing endings. For the query buy Samsung Galaxy smartphone, you will get variations like: buy Samsung Galaxy smartphone Kyiv, buy Samsung Galaxy smartphone cheap, purchase Samsung Galaxy smartphone. As we see, the city name and the word “cheap” were added to your phrase, and the word “buy” was changed to its synonym – purchase.
So, you review the results in order and select the queries you need or copy all of them directly into an Excel document, where you can quickly filter out unnecessary queries and extremely low-frequency queries (frequency less than 20 queries per month) in a more convenient format.
Selecting keywords also requires careful analysis. Put yourself in the visitor’s shoes to understand what they are looking for. For example, if you sell women’s clothing and have a query “red dress” in your list, you need to understand that the user may not necessarily want to buy that red dress. It’s possible they just want to see photos. In contrast, the query “buy red dress” would be much more suitable for you.
Once you have selected your list of key queries, you can proceed to the negative keywords stage if you are creating an advertising campaign. You can read about how to do this in this article.
ORDER contextual advertising setup
Now you’ve learned how to select keywords for your website. The process undoubtedly requires perseverance and analytical abilities, but technically, there’s nothing too difficult about it. We wish you success in mastering it.
